plant based nanoparticles
They are non-toxic have tissue-specific targeting properties and can be mass-produced. Plant-based NPs are highly stable and their synthesis is progressively quick as compared to nanoparticles synthesized by bacteria and fungi Singh et.

A Review On Plant Extract Based Route For Synthesis Of Cobalt Nanoparticles Photocatalytic Electrochemical Sensing And Antibacterial Applications Sciencedirect
Recently biological nanoparticles were found to be more pharmacologically active than physicochemically synthesized nanoparticles.

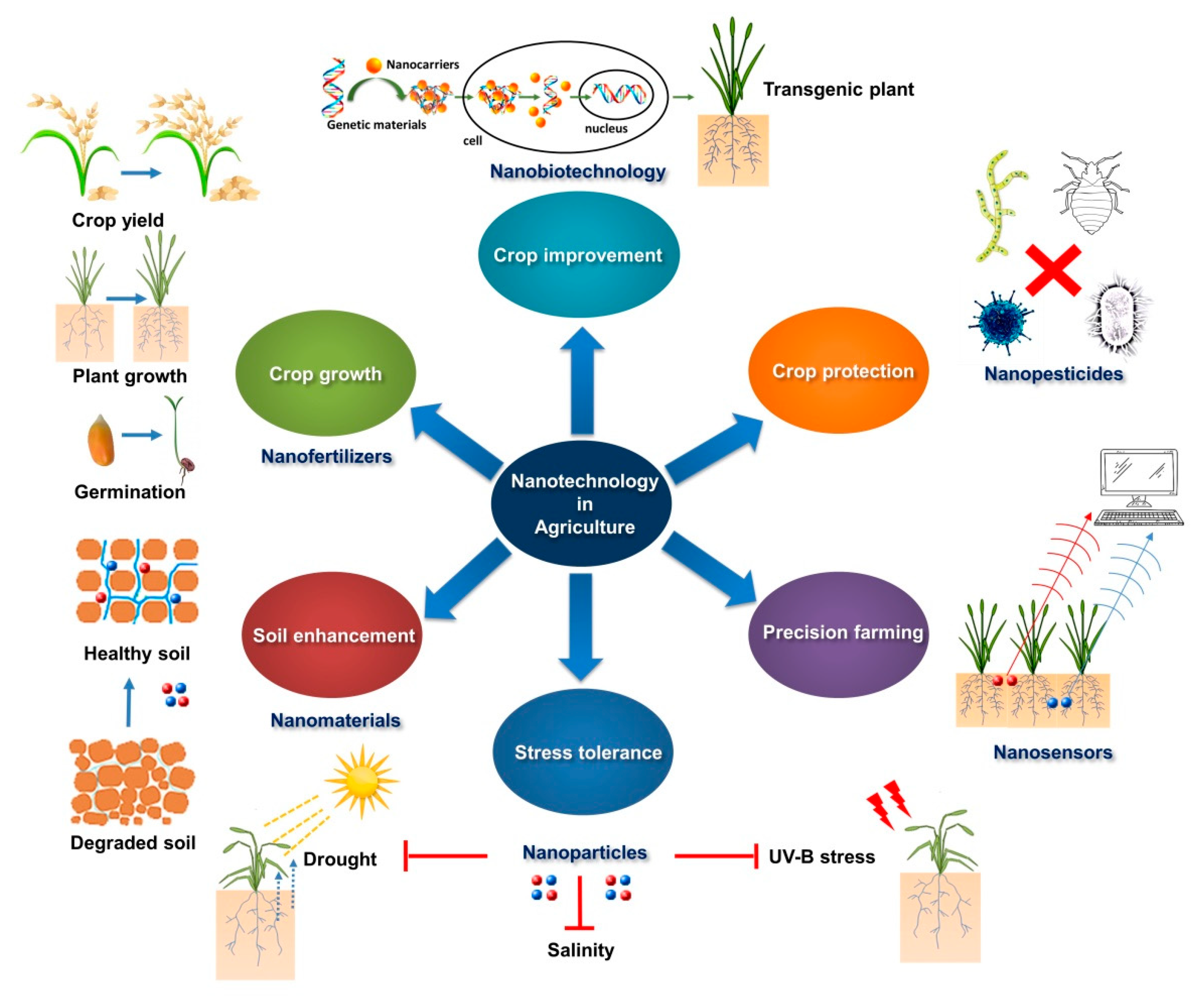
. Thus they are suitable for large-scale biosynthesis of nanoparticles. Our study uncovers that nanoparticle shape and size both greatly influence nanoparticle uptake in plant cells and the ability of plants to use the delivered biological cargoes with a strict 20 nm. ZnONPs may be made from a variety of plant components including flowers roots seeds and leaves.
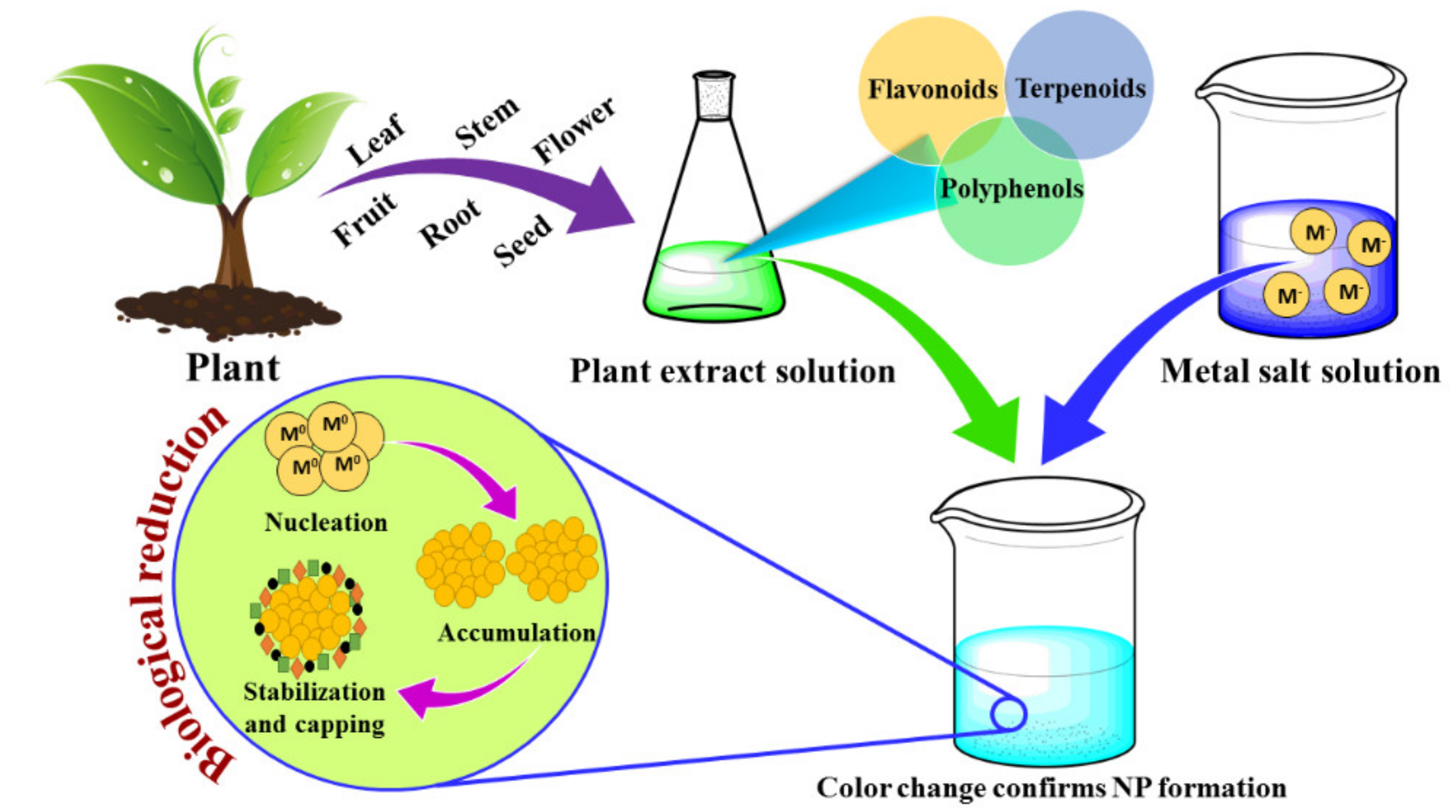
Researchers from Tokyo. Metal nanoparticles produced using microorganisms and plant extracts are stable and can be monodispersed by controlling synthetic parameters such as pH temperature incubation period and mixing ratio. Iii termination is the last phase during which NPs attain their.
Remarkably these nanoparticles exhibit a high exciton binding energy of 60 meV and a huge bandgap of 337 eV giving them a wide range of semiconducting properties. It is evident from the earlier reports that plants are the better candidates for synthesis of nanoparticles as nanoparticles produced by using plants parts are more stable and also the rate of synthesis is faster than in the case of microorganisms Iravani 2011. They have captured the attention of researchers owing to their economical sustainable green and eco-friendly nature.
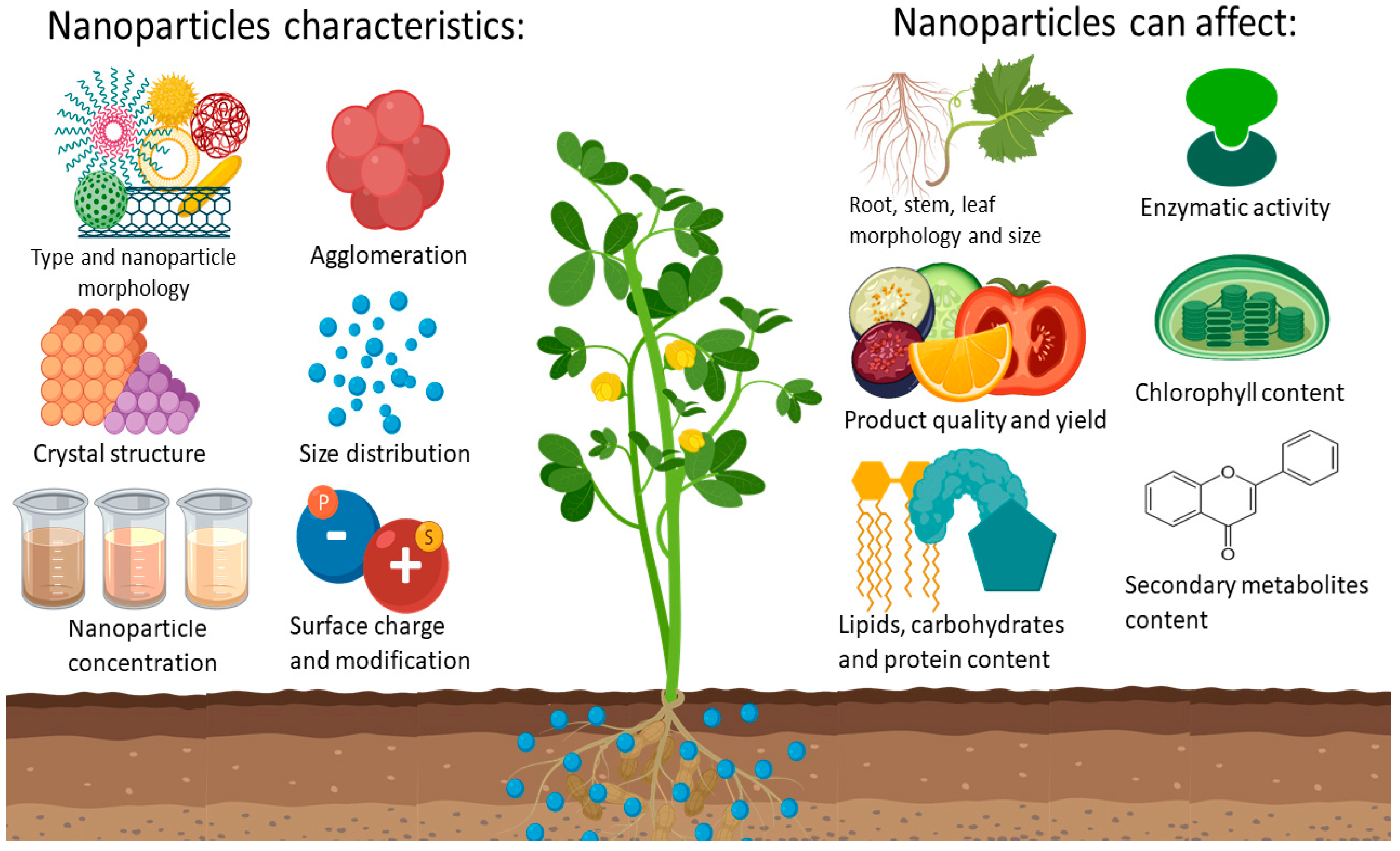
Nanoparticle traits and plant species greatly affect the interaction and nanodevices can enter and move through different pathways apoplast vs. In addition to their large availability and relatively low cost plant proteins offer higher possibilities for surface modifications and functionalizing various biomolecules for specific applications. Ii during growth phase small NPs adhere to form large size NP Ostwald ripening.
PDNPs off Recent Review Articles. Thus plant-based AgZnO nanoparticles can take up or function by biomolecules of plant extracts which can be exploited as a natural linker for drug delivery to the specified sites. The biostable capability of biosynthesized silver-zinc oxide bimetallic nanoparticles headed to healthy and unhealthy cells building them more certain as a vector for delivering drugs.
Another recently developed option is plant-derived nanoparticles NPs which can be conveniently produced in large quantities at a low cost. The study of cytotoxic and genotoxic impacts of silver nanoparticles below 100 nm size using root tip cells of Allium cepa shows that higher. However less attention has been given to Mn3O4.
In recent years there has been an outburst of interest regarding the employment of nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Symplast what influences their effectiveness and their final fate. Nanomaterials have revolutionized the world of cancer therapy and plant-derived nanoparticles have the added advantage of being cost-effective and easy to mass produce.
A team of researchers from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University obtained magnetic nanoparticles using sweet flag Acorus calamus. Plant virus nanoparticles VNPs are inexpensive to produce safe biodegradable and efficacious as treatments. Depending on the effect we are expecting for a nanocarrier the application method might be critical.
Nanoparticles from plant proteins are preferred over carbohydrates and synthetic polymeric-based materials for food medical and other applications. These nanoparticle-based systems like EVs contain bioactive molecules such as polyphenols known antioxidants and microRNA and they can deliver drugs to specific organs in thebodies. Among the different types such as metallic organic biological and hybrid systems virus based nanoparticles have become.
The applications of r plant virus nanoparticles range from epitope carriers for vaccines to agents in cancer immunotherapy. Plant-Based Nanoparticles Could Eventually Replace Some Antibiotics Many researchers reported the adverse effect of nanoparticles on plant function some of which are discussed below. Both the roots and the leaves of this plant have antioxidant.
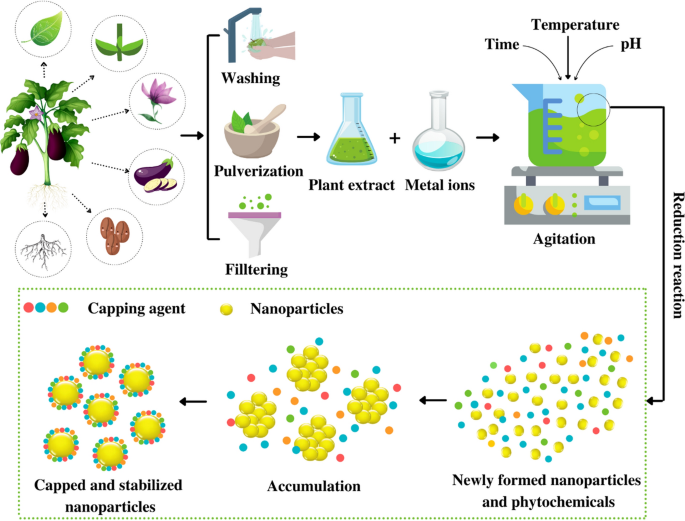
The study of plant nanotechnology receives an advantage from the great progress of nanotechnology in biomedical sciences particularly the well-development of a variety of biocompatible nanoparticles NPs and advanced analytical techniques. Biogenic Pd-based NPs from plant extracts have been identified as valuable nanocatalysts in various catalytic reactions because of their excellent activities and selectivity. I first of all reduction in metal ions takes place by the phytoconstituents followed by nucleation of reduced metal atoms that is called activation phase.
General mechanism involved in plant-based NP formation is proposed as. Thus they have great potential for clinical applications. Plant-derived edible nanoparticles PDNPs are nano-sized membrane vesicles released by edible plants such as grapefruit ginger broccoli and lemon.
Experiments on plant-derived approaches of bimetallic nanoparticles have helped describe novel passages for the production of ranging sizes and morphological shapes of NPs such as cube rhombic dodecahedron tetrahedron octahedron and spherical irregular and crystal-shaped nanomaterials 22. Nowadays green synthesis of nanoparticles using plant precursors has been extensively studied.

6 Workflow For Green Synthesis Of Nanoparticles Using Plant Leaf Extract Download Scientific Diagram
Catalysts Free Full Text Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications And Limitations Html

Silver Nanoparticle An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Molecules Free Full Text Applications Of Nanotechnology In Plant Growth And Crop Protection A Review Html
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Nanoparticles In Agroindustry Applications Toxicity Challenges And Trends Html

Plant Derived Exosome Like Nanoparticles And Their Therapeutic Activities Sciencedirect
Formation Antimicrobial Activity And Biomedical Performance Of Plant Based Nanoparticles A Review Springerlink

Plant Based Gold Nanoparticles A Comprehensive Review Of The Decade Long Research On Synthesis Mechanistic Aspects And Diverse Applications Sciencedirect
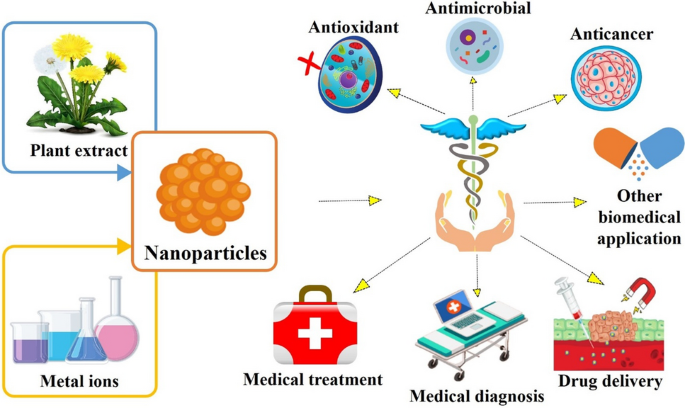
Formation Antimicrobial Activity And Biomedical Performance Of Plant Based Nanoparticles A Review Springerlink
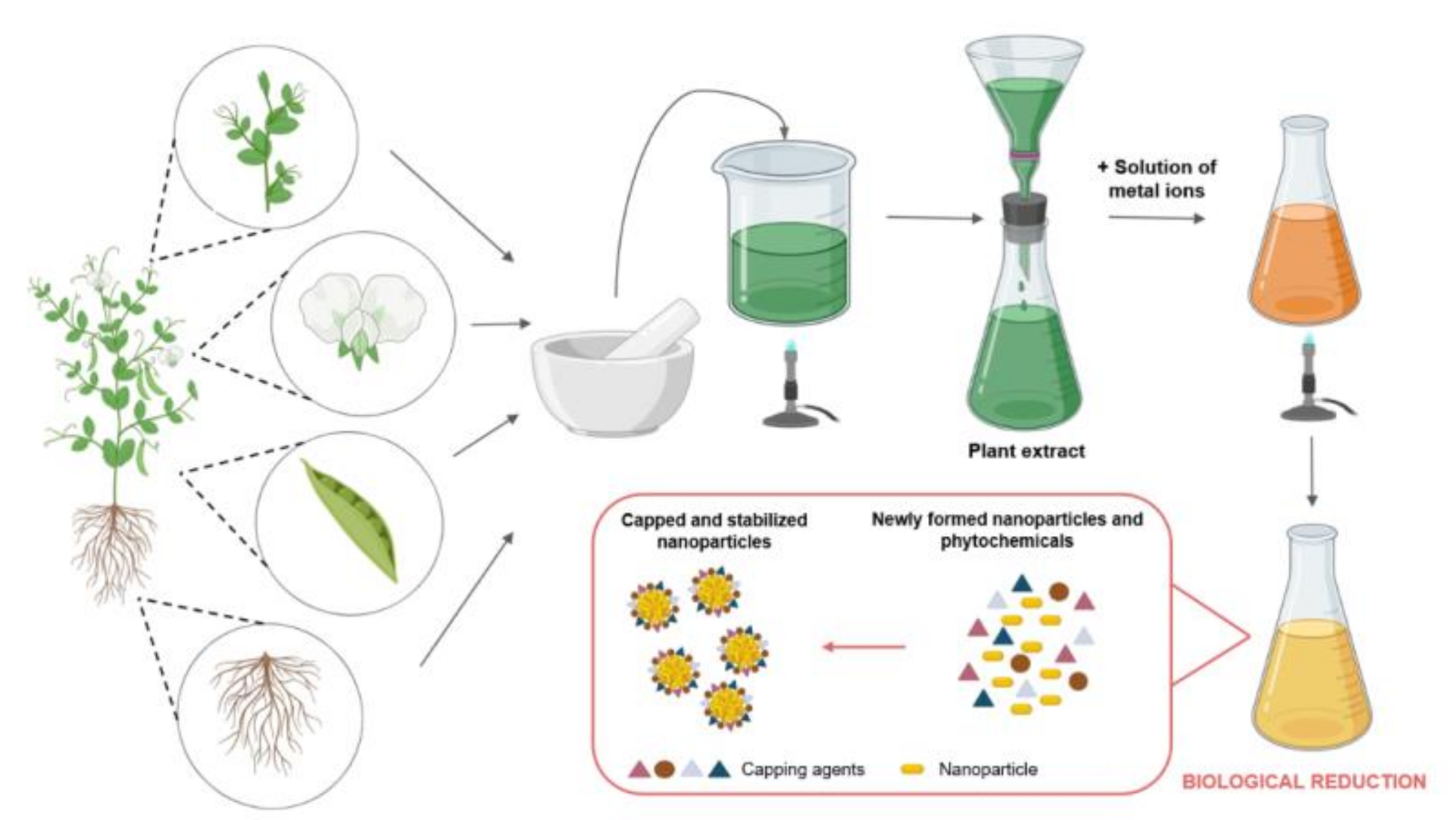
Molecules Free Full Text Green Silver And Gold Nanoparticles Biological Synthesis Approaches And Potentials For Biomedical Applications Html

Green Synthesis Of Metal And Metal Oxide Nanoparticles From Plant Leaf Extracts And Their Applications A Review
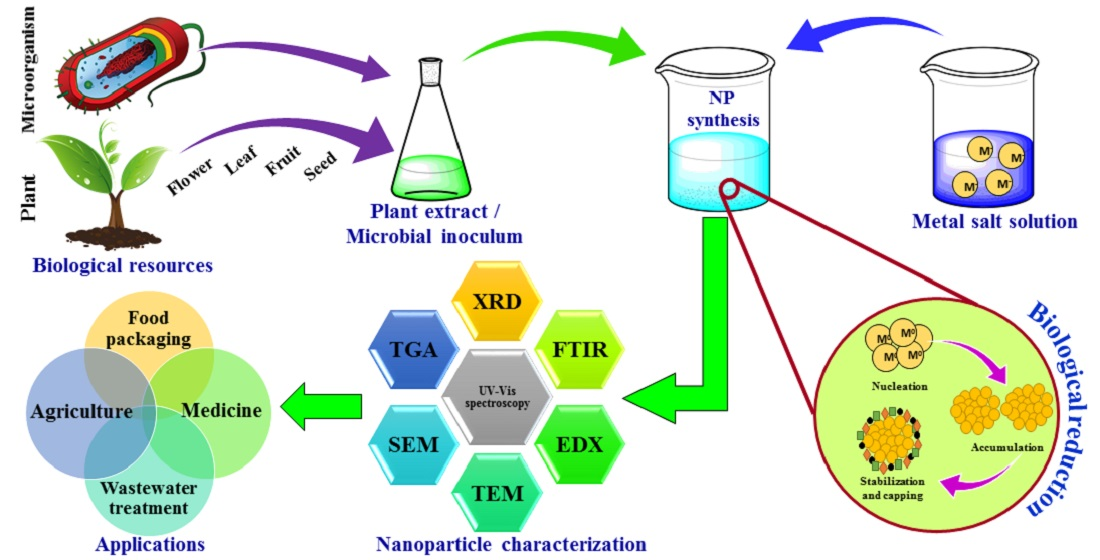
Catalysts Free Full Text Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications And Limitations Html

Plant Derived Exosome Like Nanoparticles And Their Therapeutic Activities Sciencedirect

Plant Mediated Green Synthesis Of Metal Based Nanoparticles For Dermopharmaceutical And Cosmetic Applications Sciencedirect
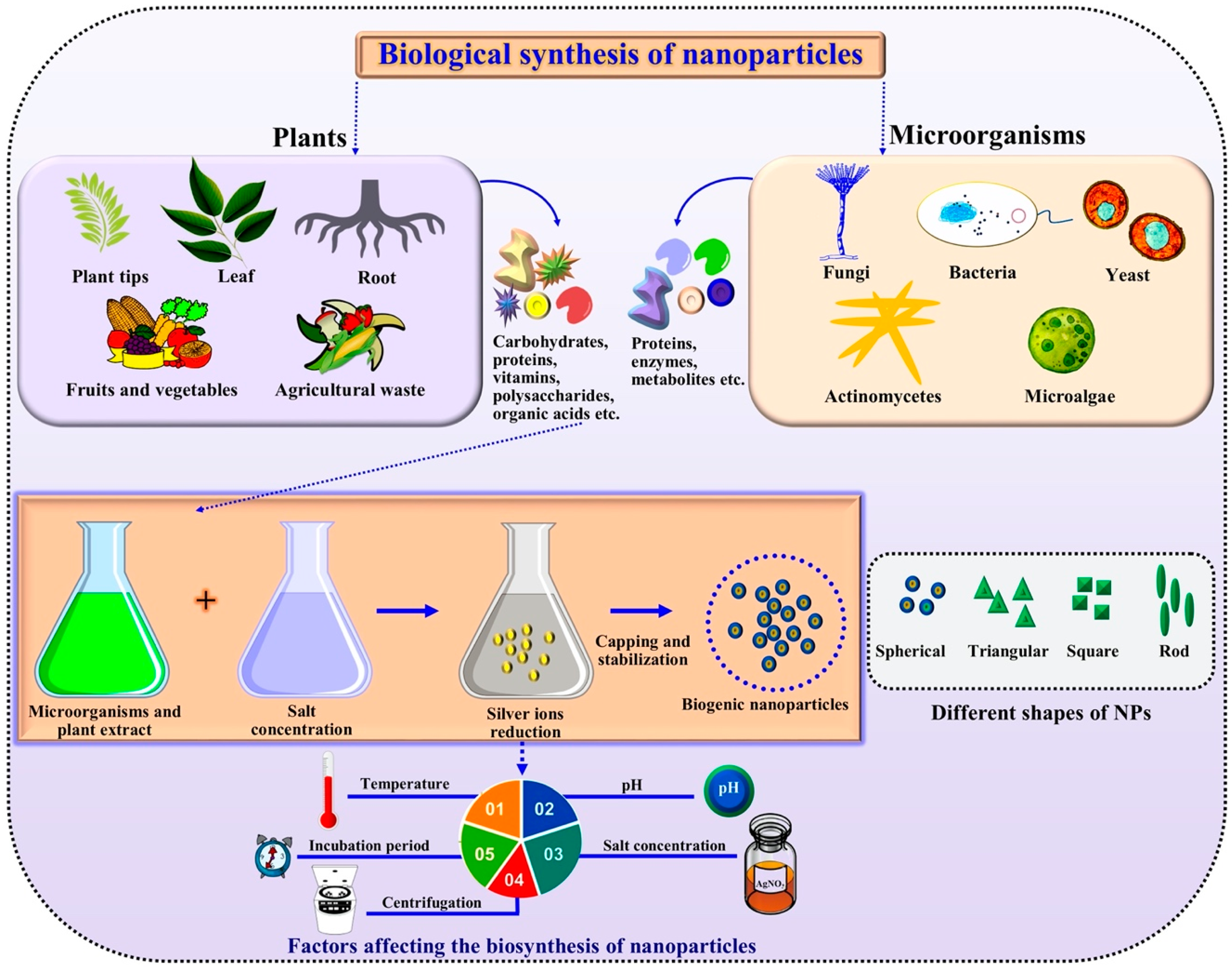
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Advancements In Plant And Microbe Based Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles And Their Antimicrobial Activity Against Plant Pathogens Html
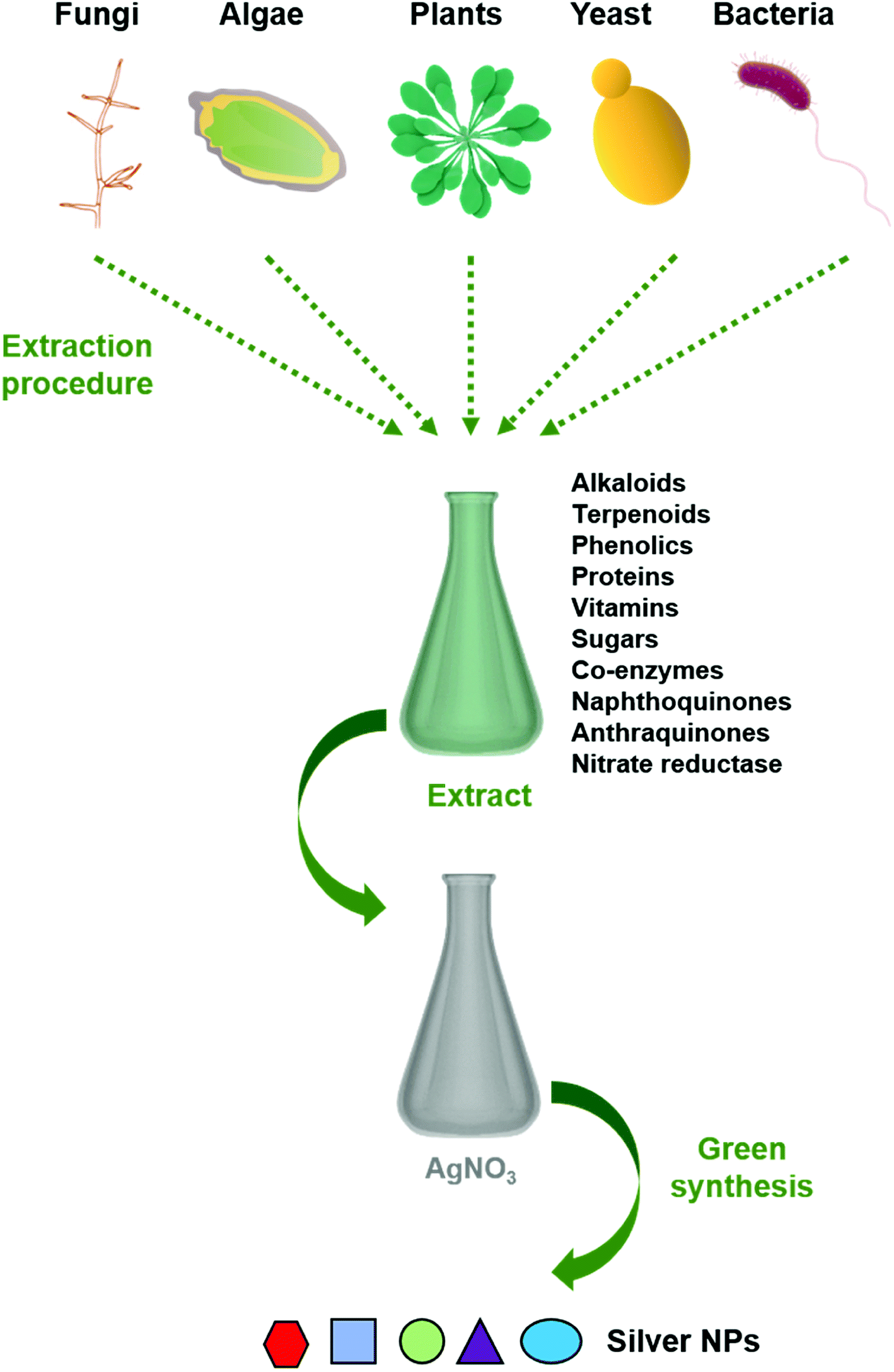
Green Synthesis Of Silver Nanoparticles Biomolecule Nanoparticle Organizations Targeting Antimicrobial Activity Rsc Advances Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C8ra08982e
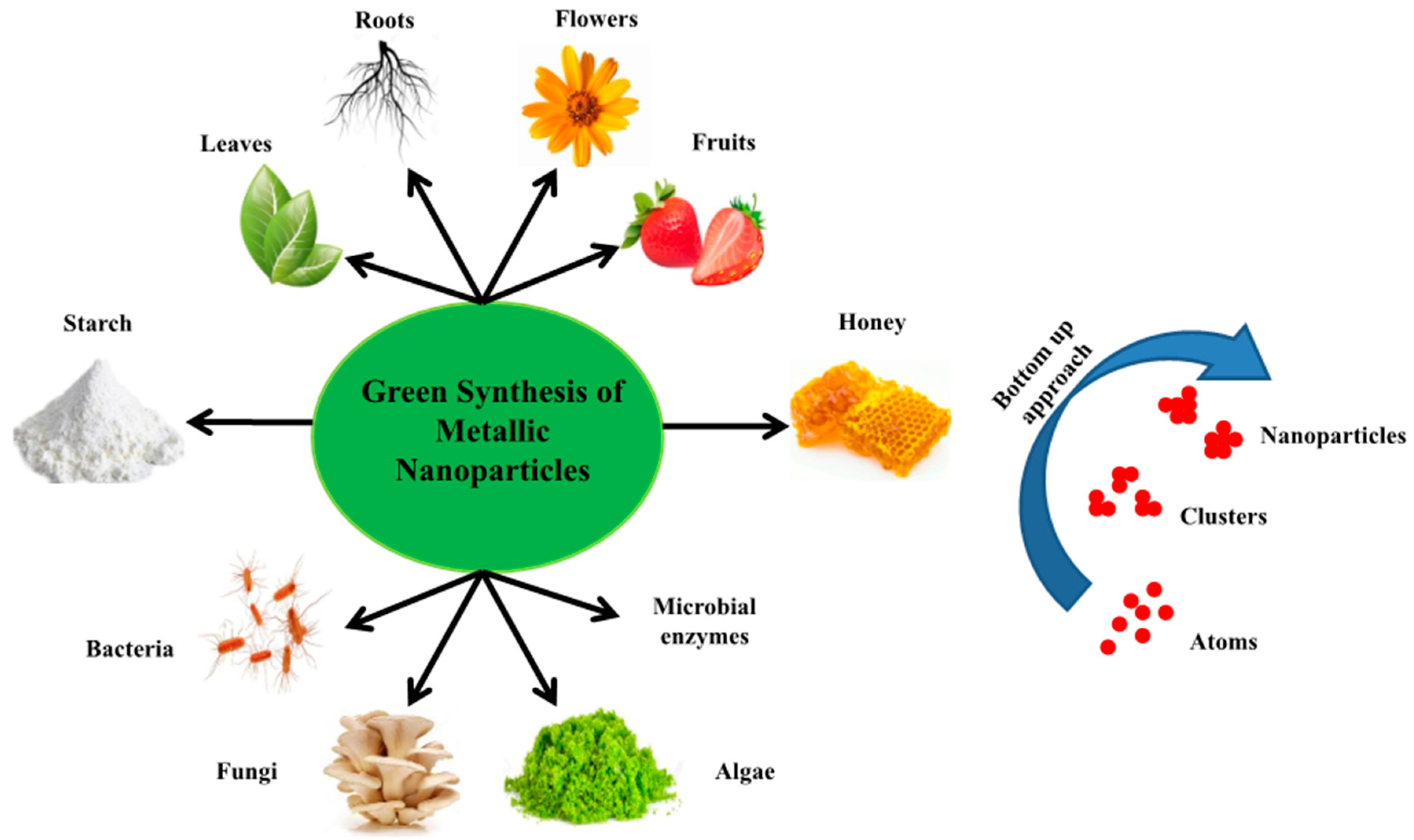
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Flower Based Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications Beyond Fragrance Html
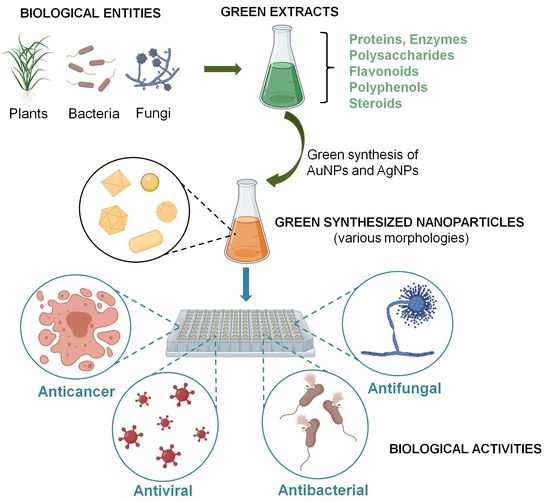
Molecules Free Full Text Green Silver And Gold Nanoparticles Biological Synthesis Approaches And Potentials For Biomedical Applications Html
Comments
Post a Comment